FeatureEffect
require(["esri/views/layers/support/FeatureEffect"], function(FeatureEffect) { /* code goes here */ });esri/views/layers/support/FeatureEffectFeatureEffect allows you to emphasize or deemphasize features that satisfy a filter in 2D MapView. The includedEffect and excludedEffect properties allow you to apply CSS filters to features that are either included or excluded from the filter. Typically, you use includedEffect to emphasize features that are included in the filter and excludedEffect to deemphasize features excluded from the filter.
Known Limitations
- The feature effect cannot be applied to a layer view with a heatmap renderer.
- FeatureEffect is not supported in layers with featureReduction of type
clusterenabled. - FeatureEffect is not supported in 3D SceneViews.
// apply feature effect to features that do not
// meet the filter requirements
featureFilter = {
// autocasts to FeatureFilter
geometry: filterGeometry,
spatialRelationship: geometryRel,
distance: distance,
units: unit
};
// set effect on excluded features
// make them gray and transparent
if (featureLayerView) {
featureLayerView.effect = {
filter: featureFilter,
excludedEffect: "grayscale(100%) opacity(30%)"
}
}
Constructors
- new FeatureEffect(properties)
- Parameter:properties Objectoptional
See the properties for a list of all the properties that may be passed into the constructor.
Example:// Typical usage const effect = new FeatureEffect({ filter:{ where: "magnitude >= 3" } excludedEffect: "grayscale(100%) opacity(30%)" }); layerView.effect = effect;
Property Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| String | The name of the class. more details | more details | Accessor | |
| Effect | The effect applied to features that do not meet the filter requirements. more details | more details | FeatureEffect | |
| Boolean | Indicates if labels for features that are excluded from the effect are visible. more details | more details | FeatureEffect | |
| FeatureFilter | The filter that drives the effect. more details | more details | FeatureEffect | |
| Effect | The effect applied to features that meet the filter requirements. more details | more details | FeatureEffect |
Property Details
The name of the class. The declared class name is formatted as
esri.folder.className.
- excludedEffect Effect
The effect applied to features that do not meet the filter requirements. Effect allows you to apply css filter-like functions to layer views to create custom visual effects to enhance the cartographic quality of your maps.
Example:const excludedEffect = "grayscale(50%) opacity(30%)"; layerView.effect = { filter: { where: "1=1", geometry: mapPoint, spatialRelationship: "disjoint", distance: searchDistance, units: searchUnit }, excludedEffect: excludedEffect };
- excludedLabelsVisible Boolean
Indicates if labels for features that are excluded from the effect are visible.
- Default Value:false
- filter FeatureFilter
The filter that drives the effect. Features that meet the requirements specified in the filter will have the includedEffect applied while features that do not meet meet the filter requirements will have the excludedEffect applied.
- includedEffect Effect
The effect applied to features that meet the filter requirements. Effect allows you to apply css filter-like functions to layer views to create custom visual effects to enhance the cartographic quality of your maps.
- See also:
Example:const includedEffect = "sepia(70%) saturate(1500%) hue-rotate(320deg) opacity(60%)"; layerView.effect = { filter: { where: "1=1", geometry: mapPoint, spatialRelationship: "disjoint", distance: searchDistance, units: searchUnit }, includedEffect: includedEffect, };
Method Overview
| Name | Return Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeatureEffect | Creates a deep clone of FeatureEffect object. more details | more details | FeatureEffect | |
| * | Creates a new instance of this class and initializes it with values from a JSON object generated from a product in the ArcGIS platform. more details | more details | FeatureEffect | |
| Object | Converts an instance of this class to its ArcGIS portal JSON representation. more details | more details | FeatureEffect |
Method Details
- clone(){FeatureEffect}
Creates a deep clone of FeatureEffect object.
Returns:Type Description FeatureEffect A new instance of a FeatureEffect
- fromJSON(json){*}static
Creates a new instance of this class and initializes it with values from a JSON object generated from a product in the ArcGIS platform. The object passed into the input
jsonparameter often comes from a response to a query operation in the REST API or a toJSON() method from another ArcGIS product. See the Using fromJSON() topic in the Guide for details and examples of when and how to use this function.Parameter:json ObjectA JSON representation of the instance in the ArcGIS format. See the ArcGIS REST API documentation for examples of the structure of various input JSON objects.
Returns:Type Description * Returns a new instance of this class.
- toJSON(){Object}
Converts an instance of this class to its ArcGIS portal JSON representation. See the Using fromJSON() guide topic for more information.
Returns:Type Description Object The ArcGIS portal JSON representation of an instance of this class.
Type Definitions
Effect provides various filter functions that can be performed on a layer or a layer view to achieve different visual effects similar to how image filters work. This powerful capability allows you to apply css filter-like functions to your layers or layer views to create custom visual effects to enhance the cartographic quality of your maps. The CSS filters are supported as effects in the API with the following differences:
- No url() css filter support.
- Only absolute length units are allowed for the effects where lengths are accepted.
- Support for bloom effect.
The following effects are supported:
bloom,blur,brightness,contrast,drop-shadow,gray-scale,hue-rotate,invert,opacity,saturateandsepia. The effect can be set in two different ways. It can be set as a string or as an array of objects.Setting effect as a string
Effects can be chained together separated by a space character. Effects are applied in the order they are set. When set as a string, the effect is applied at all scales.
// the following effect will be applied to the layer at all scales // brightness will be applied first, then hue-rotate followed by contrast // changing order of the effects will change the final result layer.effect = "brightness(5) hue-rotate(270deg) contrast(200%)";Setting effect as an array of objects
Some effects such as
bloomanddrop-shadoware sensitive to scale. Scale dependent effects should be used to fine tune or control parameters of your effects at different scales so it produces desired effects. Scale dependent effects can be set as an array of objects where you specify thescaleand the effectvaluefor that scale. When you set scale dependent effects, the API will interpolate the effects in between scales. For example, if you setopacity(0%)at one scale andopacity(100%)at another, the API will interpolate the opacity value between the scales. The type and order of effects should be consistent at all scales so that they can be interpolated. If the type and order are not consistent, the effect will be set tonull, and a warning will be shown in the console.// This is a valid scale dependent effects // at scale 4622324, the brightness will not be applied // since it is dropped. layerView.effect = { filter: featureFilter, includedEffect: [ { scale: 36978595, // small scale value: "drop-shadow(3px, 3px, 4px) brightness(400%)", }, { scale: 18489297, // large scale value: "drop-shadow(2px, 2px, 3px) brightness(200%)", }, { scale: 4622324, // larger scale value: "drop-shadow(1px, 1px, 2px)", } ], // applied at all scales excludedEffect: "brightness(80%)" }// This is an illegal scale dependent effect. // Scale dependent effects cannot be mixed like this. // No effects will be applied to the layer. // Invalid effect warning will be thrown in the console. layer.effect = [ { scale: 36978595, value: "opacity(50%)" }, { scale: 4622324, value: "brightness(500%)" } ]In the following screenshot, the left map shows the original layers without any effects. The right map shows result of the following effects being applied to two layers in the map.
// hillshade layer is displayed under the water color layer hillShadelayer.effect = "saturate(400%) contrast(100%) blur(10px)"; waterColorLayer.effect = "sepia(50%) saturate(100%) contrast(100%)";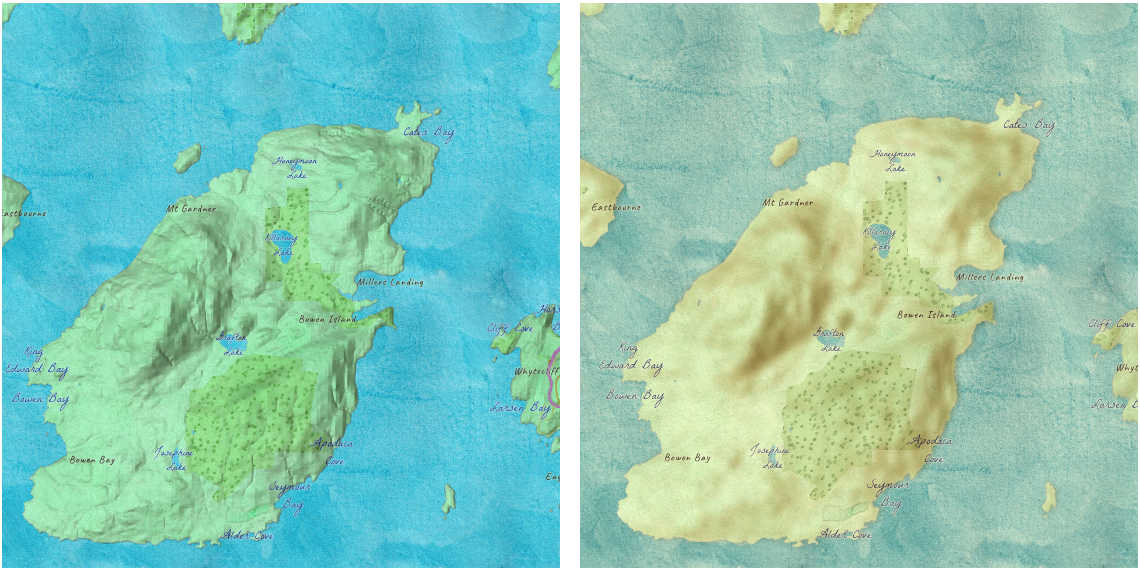
If a blendMode and an effect are used together on a layer, the effect will be applied first then the
blendMode.Read more
bloom(strength, radius, threshold) - The bloom effect produces fringes of light extending from the borders of bright areas in a layer. It causes brighter colors than the specified
thresholdto glow. You can add glow to your layers when mapping fires, volcanic eruptions and night lights.Parameter Description strength The intensity of the bloom effect. This value can percent or number. Default is 1. The higher the value, the brighter the glow. Negative values are not allowed. radius Determines the radius of the blur in an absolute length. Default value is 0. Negative values are not allowed. Leaves the features inside the radius untouched. threshold Determines how bright a color must be before it blooms or glows. Accepted values are 0%-100% or 0-1. Default value is 0. layer.effect = "bloom(200%, 1px, 0.2)"; // same as the line above layer.effect = "bloom(2, 1px, 20%)";In the following screenshot, both maps show the bombing missions of the Vietnam War (USA). On the right side, the layer does not have any effects applied. The left side shows the layer after the bloom effect is applied.
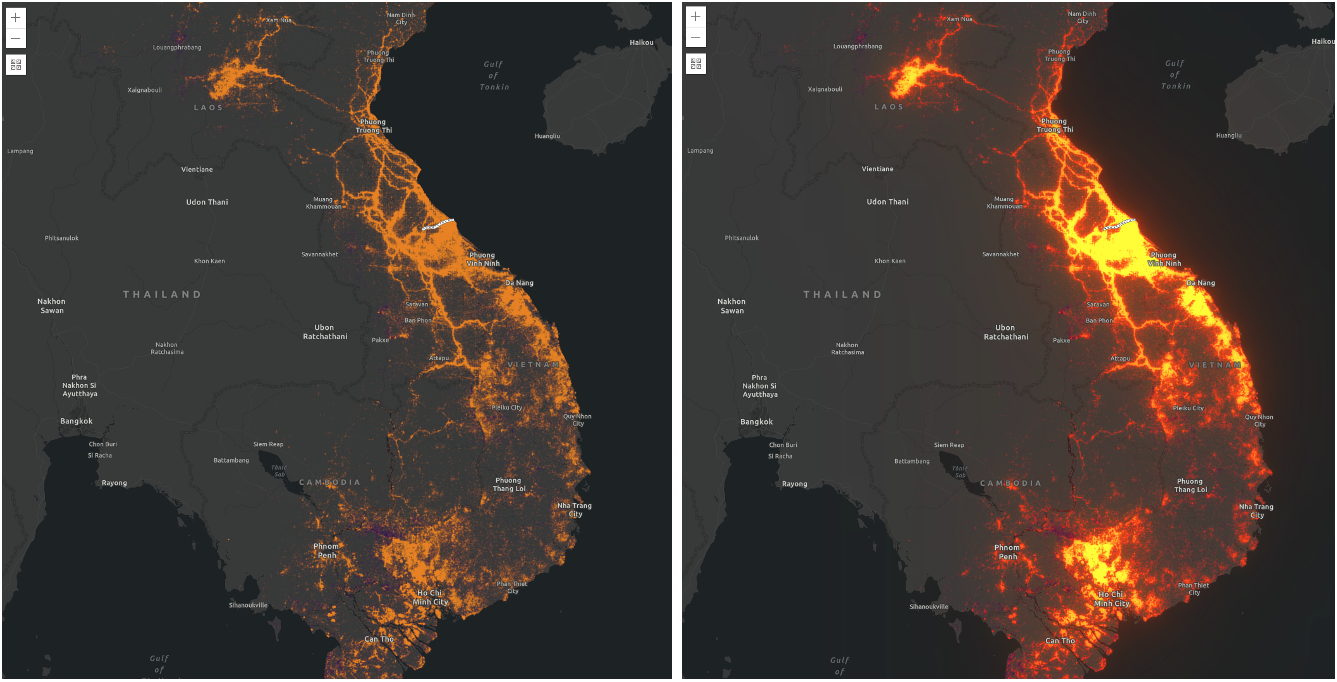
// scale dependent bloom effect is applied to US missions layer // that is shown in the above screen shot { value: "bloom(3, 1px, 0.4)", scale: 9244648.868618 }, { value: "bloom(1, 0.75px, 0.3)", scale: 4622324.434309 }, { value: "bloom(3, 0.5px, 0.2)", scale: 577790.5542885 }blur(radius) - Applies a Gaussian blur to a layer or a layer view. It makes look like you are viewing a layer through a translucent screen making it look out of focus or blurry. The
radiusparameter of the blur is specified in a absolute length. It defines how many pixels on the screen blend into each other. A larger value will create more blur. Negative values are not allowed.The
blureffect can be used to soften a layer underneath a reference layer, or other layers of importance, so above features can stand out more clearly. For a layer view, it could be used to blur out excluded features from the filter so that the included features will stand out clearly.Maps in the following screenshot show historic and current ranges of Grizzly Bears. The map on the right side is blurred to soften the edges of ranges to indicate a level of uncertainty.
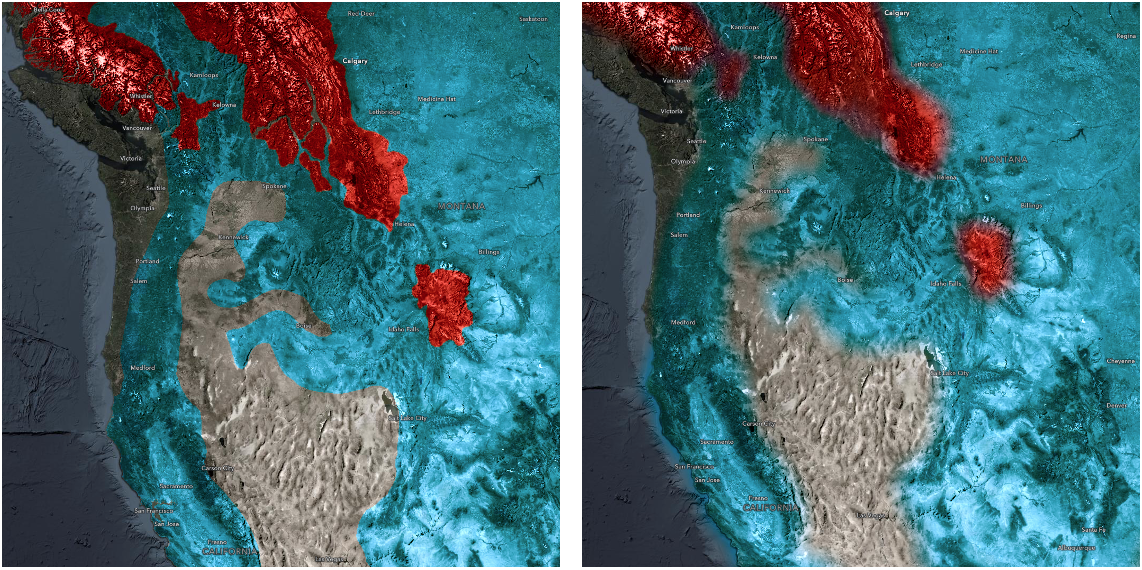
// apply effect to a layer layer.effect = "blur(5px)";// apply blur effect to excluded // features in a layer view const featureFilter = { where: `${energyType}= "coal"` }; layerView.effect = { filter: featureFilter, // apply scale dependent drop-shadow effect to // all features that satisfy the filter requirements includedEffect: [ { scale: 36978595, value: "drop-shadow(3px, 3px, 4px)" }, { scale: 18489297, value: "drop-shadow(2px, 2px, 3px)" }, { scale: 4622324, value: "drop-shadow(1px, 1px, 2px)" } ], // decrease the brightness and apply blur to the // features that do not meet filter requirements // exlcludedEffect is not scale dependent in this case excludedEffect: "blur(2px) brightness(85%)" };brightness(percent | number) - Applies a linear multiplier to a layer or a layer view, making it appear brighter or darker.
Values Effect brightness(0%) or brightness(0) Produces a completely black layer brightness(100%) or brightness(1) Unchanged layer > 100% or > 1 Brighter layer < 100% or < 1 Darker layer contrast(percent | number) – Adjusts the contrast of a layer or a layer view. Negative values are not allowed.
Values Effect contrast(0%) or contrast(0) Completely a gray layer contrast(100%) or contrast(1) Unchanged layer > 100% or > 1 More contrast in a layer < 100% or < 1 Less contrast in a layer drop-shadow(offsetX, offsetY, blurRadius?, color?) - Applies a drop shadow effect to a layer or a layer view that follows the outline of the layer or the layer view. The
drop-shadoweffect is useful when you want some features to stand out from the rest of the features on a busy map. For example, you can apply this effect to your labels (reference layer) to make them legible.Parameter Description offset-x An absolute length value that determines the shadow offset in the horizontal distance. Negative values place the shadow to the left of the layer. If both x and y offsets are 0, the shadow is placed directly underneath the layer. offset-y An absolute length value that determines the shadow offset in the vertical distance. Negative values place the shadow above the layer. blur-radius An absolute length value that determines the blur radius. The larger the value, the larger and more blurred the shadow becomes. If unspecified, it defaults to 0, resulting in a sharp, unblurred edge. Negative values are not allowed. color The color of the shadow. If unspecified, it defaults to black color. In the following screenshot, the left map shows 2019 overall index of multiple deprivation experienced by people living in a greater London area. The right map shows the result of applying
drop-shadowto features that intersect boundaries of London boroughs while applyingblurandbrightnesseffects to features do not meet from the filter criteria of FeatureEffect.const featureFilter = { where: "BoroughEdge = 'true'" }; layerView.effect = { filter: featureFilter, includedEffect: "drop-shadow(3px, 3px, 3px, black)", excludedEffect: "blur(1px) brightness(65%)" }
grayscale(percent | number) - Converts a layer or a layer view to grayscale. The value of amount defines the proportion of the conversion. If the amount parameter is missing, a value of 100% is used. Negative values are not allowed.
Values Effect grayscale(0%) or grayscale(0) Unchanged layer grayscale(100%) or grayscale(1) Completely gray layer < 100% or < 1 Varying shades of gray > 100% or > 1 Same as 100% or 1 hue-rotate(angle) - Applies a hue rotation on a layer or a layer view. The value of angle defines the number of degrees around the color wheel. The colors in the layer will be shifted to the colors at the specified angle. A value of
0degleaves the input unchanged. Maximum value is360deg. A positive hue rotation shifts the hue clock-wise while a negative rotation shifts the hue counter clock-wise.Parameter Description angle The relative change in hue of the input sample, specified as an angle such as deg,rad,gradandturn.invert(percent | number) - Inverts the samples in the layer. The value of amount defines the proportion of the conversion. Negative values are not allowed.
Values Effect invert(0%) or invert(0) Unchanged layer invert(100%) or invert(1) Completely inverted layer < 100% or < 1 Varying degrees of inversion > 100% or > 1 Same as 100% or 1 opacity(percent | number) - Applies transparency to a layer or a layer view. The value of amount defines the proportion of the conversion. Negative values are not allowed.
Values Effect opacity(0%) or opacity(0) Completely transparent layer opacity(100%) or opacity(1) Completely opaque layer < 100% or < 1 Varying degrees of opacity > 100% or > 1 Same as 100% or 1 saturate(percent | number) - Saturates or desaturates a layer or a layer view.
Values Effect saturate(0%) or saturate(0) Completely unsaturated layer saturate(100%) or saturate(1) Leaves the layer or layer view unchanged < 100% or < 1 Varying degrees of desaturation > 100% or > 1 Varying degrees of saturation sepia(percent | number) - Converts colors in a layer or a layer view to sepia, giving it a warmer, more yellow/brown appearance. Negative values are not allowed.
Values Effect sepia(0%) or sepia(0) Unchanged layer or layer view sepia(100%) or sepia(1) Completely sepia < 100% or < 1 Varying degrees of sepia > 100% or > 1 Same as 100% or 1 Known Limitations
- The effect is not supported in 3D SceneViews.
- The effect is not supported in printing and in legend.