FeatureReductionCluster
require(["esri/layers/support/FeatureReductionCluster"], function(FeatureReductionCluster) { /* code goes here */ });esri/layers/support/FeatureReductionClusterThis class configures clustering as a means of reducing and summarizing point features in a FeatureLayer, CSVLayer, GeoJSONLayer or OGCFeatureLayer. This feature reduction method spatially groups points into clusters based on an area of influence, or clusterRadius. The size of each cluster is proportional to the number of features within the cluster.
Point clustering only applies to layers with Point geometries in a MapView containing either a SimpleRenderer, UniqueValueRenderer, or a ClassBreaksRenderer. It does not apply to layers with polyline and polygon geometries.
While this can be thought of as a visualization technique, clustering is actually a method of reducing features in the view. It is therefore independent of the Renderer. The style, labels, and popup of each cluster summarizes the features it represents.
Configuration best practices
- There's no such thing as clusters with a count of one. If a feature does not belong to a cluster, it is rendered by itself according the configuration defined in the layer's renderer. If you want individual features to be smaller than the smallest clusters (two or more features), then you need to adjust the size of the symbols in the renderer to sizes smaller than the clusterMinSize.
- The maxClusterSize and clusterRadius complement each other. If you adjust one, you should adjust the other (a larger
maxClusterSizeshould have a largerclusterRadius). - Turn off label deconfliction when labeling clusters with a count in the center of the cluster. If label placement is outside the cluster, keep label deconfliction enabled.
- Increase the clusterMinSize to fit labels inside smaller clusters (16pt is a good starting point when labels are visible).
- If the layer's renderer has a SizeVariable, increase the size of the smallest features (either in the variable stops, or in the
minSizeproperty) to improve the cluster visualization, and so labels can fit inside the clusters. - If multiple label classes are set on
featureReduction.labelingInfo, set matching label classes on thelayer.labelingInfo, especially when a size visual variable is included in the renderer. This helps the end user differentiate between clusters and individual features.
Styles and configurations
See popupTemplate for information on configuring cluster popups. The following describes how each renderer type affects the style of clusters.
Expand the following section to learn about how various renderers impact the look and feel of clustered layers.
Read more
Simple Renderer
In the most basic scenario, where all points are styled with a SimpleRenderer and no visual variables, the cluster size will indicate the number of features within the cluster.
| Display all points | Display clustered features |
|---|---|
 | 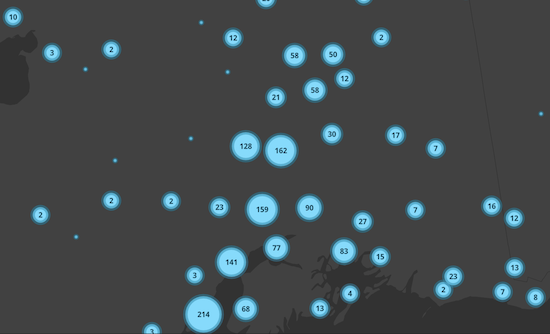 |
Visual Variables
When any numeric field is used by the renderer, either with one or more visual variables or a ClassBreaksRenderer, the average value of that field will be used in the cluster symbology and made available to the developer in the popupTemplate.
In the example below, the layer representing weather stations is rendered with three visual variables: color, size, and rotation. When clustering is enabled, the average of each field from the visual variables is computed for the features within each cluster. The color, rotation, and size of the cluster is then applied to the cluster graphic according to the average value of each respective field for the visual variables of features in that cluster.
| Display all points | Display clustered features |
|---|---|
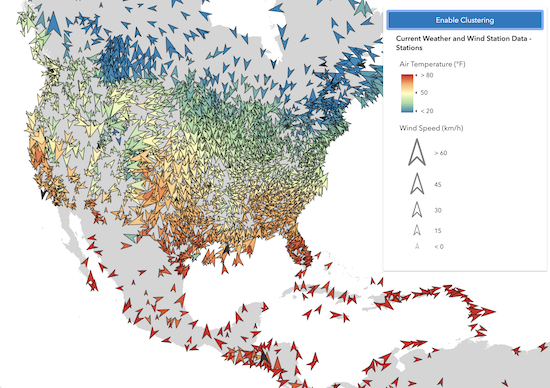 | 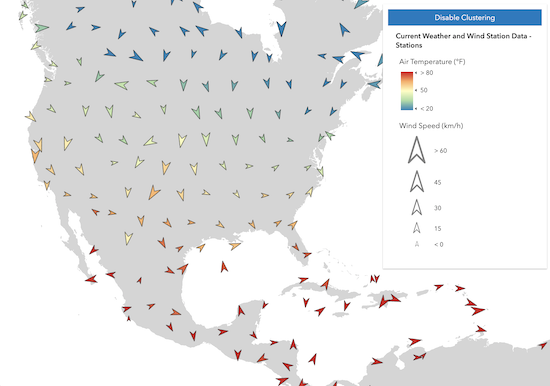 |
Unique Value Renderer
When a clustered layer contains a UniqueValueRenderer, the clustered graphics are rendered with the symbol of the most common, or predominant, value of the uniqueValueInfos of the features represented by the cluster.
| Display all points | Display clustered features |
|---|---|
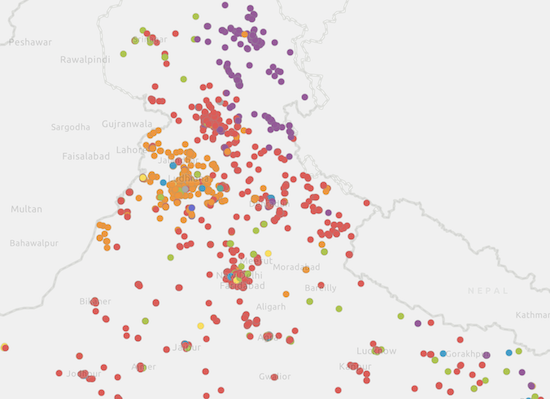 | 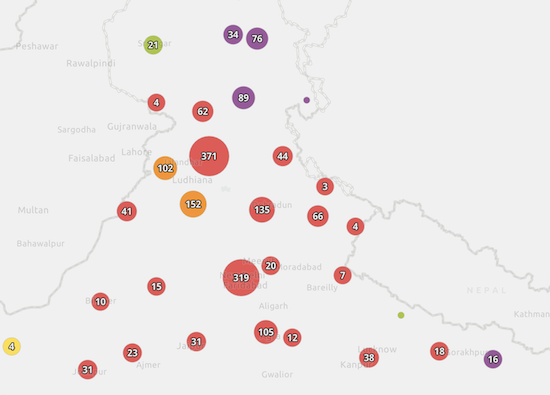 |
Known Limitations
Clustering currently has the following limitations:
- Not supported in 3D SceneView.
- Not supported in MapImageLayer.
- Layers with a UniqueValueRenderer may not contain multiple fields (i.e. field2, field3).
- Layer views with an applied FeatureEffect cannot be clustered.
- Clustering layers with spatial references other than Web Mercator and WGS-84 is experimental and may not work for every projection. Clustered layers that have spatial references other than Web Mercator or WGS-84, have the same limitations listed in the projection engine documentation.
- See also:
layer.featureReduction = {
type: "cluster",
clusterRadius: "120px",
popupTemplate: {
content: "This cluster represents <b>{cluster_count}</b> features.",
fieldInfos: [{
fieldName: "cluster_count",
format: {
digitSeparator: true,
places: 0
}
}]
}
};Constructors
- new FeatureReductionCluster(properties)
- Parameter:properties Objectoptional
See the properties for a list of all the properties that may be passed into the constructor.
Property Overview
| Name | Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Defines the symbol size of the largest cluster in points (or pixels if specified). more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| Number | Defines the symbol size of the smallest cluster in points (or pixels if specified). more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| Number | Defines the radius in points (or pixels if specified) of each area in which multiple points will be grouped and visualized as a single cluster. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| String | The name of the class. more details | more details | Accessor | |
| LabelClass[] | Defines labels for clusters as an array of LabelClass. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether to display labels for the clusters. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| Boolean | Indicates whether to display the cluster popup. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| PopupTemplate | The PopupTemplate to apply to clustered graphics. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| String | The feature reduction type. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster |
Property Details
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.16
Defines the symbol size of the largest cluster in points (or pixels if specified). Adjusting
clusterMaxSizegenerally should be considered if the clusterRadius is modified.For example, if you prefer cluster icons to not overlap, then the
clusterMaxSizeshould be substantially smaller than theclusterRadius.- Default Value:37.5
- See also:
Example:// clusterMaxSize should be adjusted // appropriately to conform // to the clusterRadius layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", clusterRadius: "50px", clusterMaxSize: "32px" };
- Since: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.16
Defines the symbol size of the smallest cluster in points (or pixels if specified). If labeling clusters with a count or some other information in the center of the cluster, then having a
clusterMinSizelarger than the default is generally preferred.Keep in mind that this size may be smaller than the symbol size of individual non-clustered features in the layer. In that scenario, you should either reduce the size of the symbol(s) in the layer's renderer or increase the
clusterMinSizeto be larger than the size of individual points to avoid confusion for the end user. This can most likely happen when cluster size represents feature count.- Default Value:9
- See also:
Example:// a larger clusterMinSize looks better when labels are enabled featureReduction.clusterMinSize = "24px"; featureReduction.labelsVisible = true;
Defines the radius in points (or pixels if specified) of each area in which multiple points will be grouped and visualized as a single cluster. Adjusting
clusterRadiusgenerally should be considered if the clusterMaxSize is modified.For example, if you prefer cluster icons to not overlap, then the
clusterRadiusshould be substantially larger than theclusterMaxSize.- Default Value:60
- See also:
Examples:// enables clustering on the layer with a // clusterRadius of 40pt layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", clusterRadius: 40, clusterMaxSize: 24 };// enables clustering on the layer with a // clusterRadius of 120px layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", clusterRadius: "120px", clusterMaxSize: "80px" };
The name of the class. The declared class name is formatted as
esri.folder.className.
- labelingInfo LabelClass[]autocastSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.16
Defines labels for clusters as an array of LabelClass. When set, labels independent of the layer.labelingInfo are used to convey information about the clusters, including the count of all features in the cluster, the average, or predominant values of fields mapped by the renderer.
It is advisable to turn off label deconfliction when labeling clusters with a count in the center of the cluster. To generate suggested labels for your cluster configuration based on the layer's renderer, see clusterLabelCreator.
The table below describes the aggregate fields used internally by the cluster renderer, which you can reference in the label expression.
Aggregate fields:
Field Name Type Description cluster_countnumber The number of features in the cluster. cluster_avg_{fieldName}number For renderers visualizing a number field either with size, opacity, continuous color, or class breaks, this field describes the average of the rendered field among all features in the cluster. cluster_type_{fieldName}string For layers with a UniqueValueRenderer, this field describes the mode, or predominant string of the rendered field among all features within the cluster. Multiple Label classes with different
whereclauses can be used to define several labels with varying styles on the same feature. Likewise, multiple label classes may be used to label different types of clusters (e.g. blue labels for small clusters and red labels for large ones).- See also:
Example:// Displays the count inside the cluster layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", labelingInfo: [{ labelExpressionInfo: { expression: "$feature.cluster_count" }, deconflictionStrategy: "none", labelPlacement: "center-center", symbol: { type: "text", color: "white", font: { size: "12px" }, haloSize: 1, haloColor: "black" } }] };
- labelsVisible BooleanSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.16
Indicates whether to display labels for the clusters. If
true, labels will appear as defined in the labelingInfo property.- Default Value:true
Example:// Turns off cluster labels, but preserves labelingInfo const featureReduction = layer.featureReduction.clone(); featureReduction.labelsVisible = false; layer.featureReduction = featureReduction;
- popupEnabled BooleanSince: ArcGIS API for JavaScript 4.16
Indicates whether to display the cluster popup. If
true, popups will open when the user clicks or taps a cluster. Iffalse, the popup as defined in the popupTemplate will be persisted, but won't be displayed on click/tap.- Default Value:true
Example:// Turns off cluster popups, but preserves popupTemplate const featureReduction = layer.featureReduction.clone(); featureReduction.popupEnabled = false; layer.featureReduction = featureReduction;
- popupTemplate PopupTemplateautocast
The PopupTemplate to apply to clustered graphics. When set, a popupTemplate independent of the layer.popupTemplate is used. This popup can display summary information for the cluster, including the count of all features in the cluster and the average or predominant values of fields mapped by the renderer.
To generate a suggested predefined popup template for your cluster configuration based on the layer's renderer, see clusterPopupTemplateCreator.
The table below describes the aggregate fields used internally by the cluster renderer, which you can reference in the cluster popup.
Aggregate fields:
Field Name Type Description cluster_countnumber The number of features in the cluster. cluster_avg_{fieldName}number For renderers visualizing a number field either with size, opacity, continuous color, or class breaks, this field describes the average of the rendered field among all features in the cluster. cluster_type_{fieldName}string For layers with a UniqueValueRenderer, this field describes the mode, or predominant string of the rendered field among all features within the cluster. The following
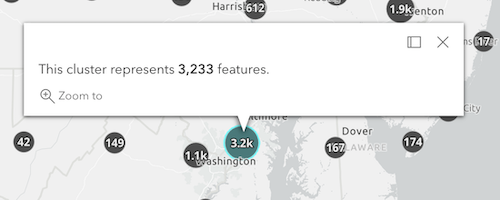
popupTemplateconfigurations will display the popups shown in the images below.Cluster count
layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", popupTemplate: { content: "This cluster represents {cluster_count} earthquakes." } };Clusters by predominant type
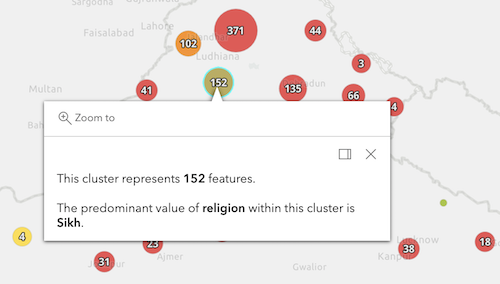
The following featureReduction configuration assumes the layer's renderer is a UniqueValueRenderer who's field is named
religion.layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", popupTemplate: { content: [{ type: "text", text: "This cluster represents <b>{cluster_count}</b> features." }, { type: "text", text: "The predominant place of worship in this cluster is <b>{cluster_type_religion}</b>." }] } };Clusters with visual variables
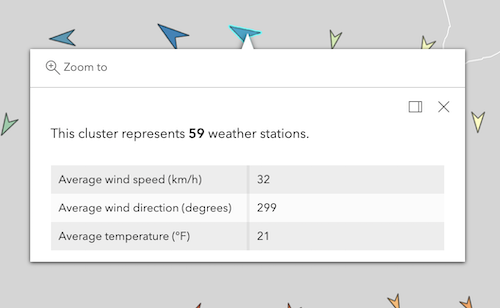
The following featureReduction configuration assumes the layer's renderer contains visual variables referencing fields named
WIND_SPEED,WIND_DIRECT,TEMP.layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", popupTemplate: { content: [{ type: "text", text: "This cluster represents <b>{cluster_count}</b> weather stations." }, { type: "fields", fieldInfos: [{ fieldName: "cluster_avg_WIND_SPEED", label: "Average wind speed (km/h)", format: { places: 0 } }, { fieldName: "cluster_avg_WIND_DIRECT", label: "Average wind direction (degrees)", format: { places: 0 } }, { fieldName: "cluster_avg_TEMP", label: "Average temperature (°F)", format: { places: 0 } }] }] } };Known Limitations
Aggregate fields referring to values in renderers calculated with a
normalizationFieldorvalueExpressionare not supported. Support for these scenarios is coming at a future release.- See also:
Examples:// enables clustering on the layer with a // popup describing the number of features represented by each cluster layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", popupTemplate: { content: "This cluster represents <b>{cluster_count}</b> features." fieldInfos: [{ fieldName: "cluster_count", format: { digitSeparator: true, places: 0 } }] } };// enables clustering on the layer with a // popup describing the average value of // the field mapped by the renderer layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster", renderer: { type: "simple", symbol: { type: "simple-marker", size: 8 }, label: "Weather stations", visualVariables: [ { type: "color", field: "Temperature", stops: [ { value: 32, color: "blue", label: "< 32° F" }, { value: 90, color: "red", label: ">90° F" } ] } ] }; popupTemplate: { content: [{ type: "text", text: "This cluster represents <b>{cluster_count}</b> features." }, { type: "text", text: "The average temperature in this cluster is <b>{cluster_avg_Temperature}° F</b>." }], fieldInfos: [{ fieldName: "cluster_count", format: { digitSeparator: true, places: 0 } }, { fieldName: "cluster_avg_Temperature", format: { places: 1 } }] } };
- type String
The feature reduction type.
For FeatureReductionCluster the type is always "cluster".
Example:// enables clustering on the layer with the default // clusterRadius (80px) layer.featureReduction = { type: "cluster" };
Method Overview
| Name | Return Type | Summary | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeatureReductionCluster | Creates a deep clone of the FeatureReductionCluster object. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| * | Creates a new instance of this class and initializes it with values from a JSON object generated from a product in the ArcGIS platform. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster | |
| Object | Converts an instance of this class to its ArcGIS portal JSON representation. more details | more details | FeatureReductionCluster |
Method Details
- clone(){FeatureReductionCluster}
Creates a deep clone of the FeatureReductionCluster object.
Returns:Type Description FeatureReductionCluster A deep clone of the object that invoked this method. Example:// Creates a deep clone of the feature reduction object const fr = layer.featureReduction.clone(); fr.clusterMinSize = 18; layer.featureReduction = fr;
- fromJSON(json){*}static
Creates a new instance of this class and initializes it with values from a JSON object generated from a product in the ArcGIS platform. The object passed into the input
jsonparameter often comes from a response to a query operation in the REST API or a toJSON() method from another ArcGIS product. See the Using fromJSON() topic in the Guide for details and examples of when and how to use this function.Parameter:json ObjectA JSON representation of the instance in the ArcGIS format. See the ArcGIS REST API documentation for examples of the structure of various input JSON objects.
Returns:Type Description * Returns a new instance of this class.
- toJSON(){Object}
Converts an instance of this class to its ArcGIS portal JSON representation. See the Using fromJSON() guide topic for more information.
Returns:Type Description Object The ArcGIS portal JSON representation of an instance of this class.